Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster with Minikube on Debian 11
I’m using a Hetzner dedicated server here, but a VPS works as well.
CPU 型号 : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700 CPU @ 3.60GHz CPU 核心数 : 1 物理核心, 4 总核心, 8 总线程数 CPU 频率 : 4089.603 MHz CPU 缓存 : L1: 256.00 KB / L2: 1.00 MB / L3: 8.00 MB 硬盘空间 : 678.17 GiB / 936.60 GiB 启动盘路径 : /dev/md1 内存 : 24.31 GiB / 62.59 GiB Swap : [ no swap partition or swap file detected ] 系统在线时间 : 14 days, 19 hour 25 min 负载 : 1.42, 1.76, 2.01 系统 : Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye) (x86_64) AES-NI指令集 : ✔ Enabled VM-x/AMD-V支持 : ✔ Enabled 架构 : x86_64 (64 Bit) 内核 : 5.10.0-23-amd64 TCP加速方式 : bbr 虚拟化架构 : Dedicated NAT类型 : 开放型 IPV4 ASN : AS24940 Hetzner Online GmbH IPV4 位置 : Berlin / Berlin / DE IPV6 ASN : AS24940 Hetzner Online GmbH IPV6 位置 : Nuremberg / DE-BYEnvironment preparation
2 CPUs or more
2GB of free memory
20GB of free disk space
Internet connection
Container or virtual machine manager, such as: Docker, QEMU, Hyperkit, Hyper-V, KVM, Parallels, Podman, VirtualBox, or VMware Fusion/Workstation
Install Kubectl
依次执行curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"chmod +x ./kubectlsudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
### 检查Kubectl是否安装成功kubectl version -o yaml
Install Minikube
依次执行curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-darwin-amd64sudo install minikube-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube检查是否安装成功minikube version
Start Minikube
我这边采用的是Root权限下启动需要执行的,如果直接minikube启动,会有权限警告错误minikube start --driver=docker --force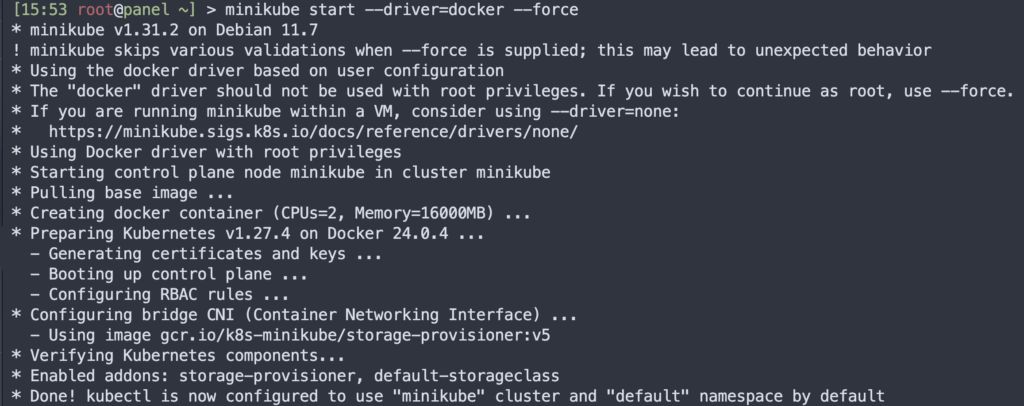
Error summary
When logged in as root, starting the cluster directly with minikube start shows:
minikube v1.31.2 on Debian 11.7Automatically selected the docker driver. Other choices: ssh, noneThe "docker" driver should not be used with root privileges. If you wish to continue as root, use --force.If you are running minikube within a VM, consider using --driver=none:https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/reference/drivers/none/X Exiting due to DRV_AS_ROOT: The "docker" driver should not be used with root privileges.Solutions:
- Switch to a non-root user.
- Start the cluster with
minikube start --driver=docker --force.
Check cluster status
kubectl cluster-info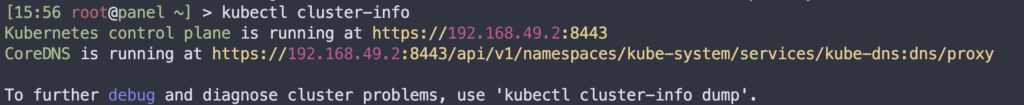
Check running nodes
kubectl get nodes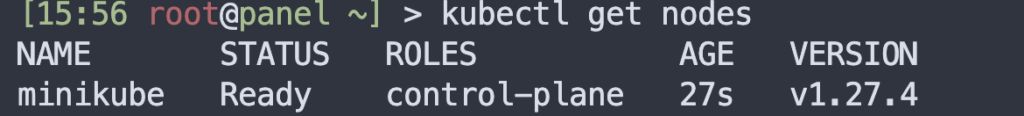
Access the Minikube container
minikube ssh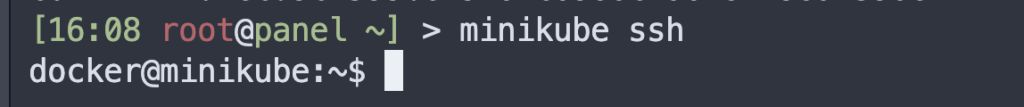
Exit the container shell:
exit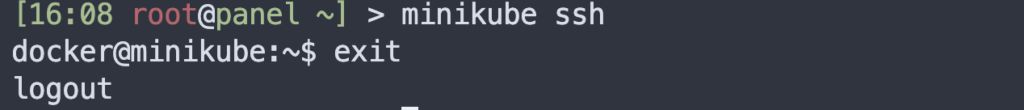
Stop and delete the Kubernetes cluster
minikube stopminikube deleteCheck Minikube status
minikube status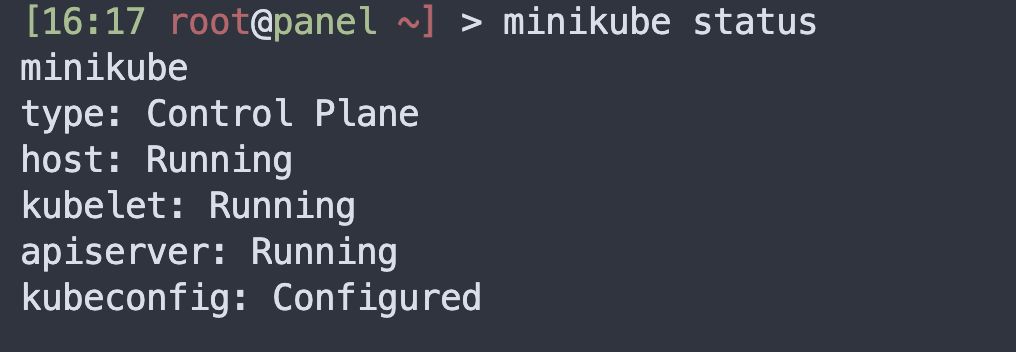
Access the Minikube Kubernetes Dashboard
By default, Minikube provides a web UI you can use to manage your cluster.
You can list all Minikube addons with the following command: minikube addons list
You’ll see output similar to this:
[15:56 root@panel ~] > minikube addons list|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|| ADDON NAME | PROFILE | STATUS | MAINTAINER ||-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|| ambassador | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Ambassador) || auto-pause | minikube | disabled | minikube || cloud-spanner | minikube | disabled | Google || csi-hostpath-driver | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes || dashboard | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes || default-storageclass | minikube | enabled ✅ | Kubernetes || efk | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Elastic) || freshpod | minikube | disabled | Google || gcp-auth | minikube | disabled | Google || gvisor | minikube | disabled | minikube || headlamp | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (kinvolk.io) || helm-tiller | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Helm) || inaccel | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (InAccel || | | | [info@inaccel.com]) || ingress | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes || ingress-dns | minikube | disabled | minikube || inspektor-gadget | minikube | disabled | 3rd party || | | | (inspektor-gadget.io) || istio | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Istio) || istio-provisioner | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Istio) || kong | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Kong HQ) || kubevirt | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (KubeVirt) || logviewer | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) || metallb | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (MetalLB) || metrics-server | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes || nvidia-driver-installer | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Nvidia) || nvidia-gpu-device-plugin | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Nvidia) || olm | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Operator Framework) || pod-security-policy | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) || portainer | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Portainer.io) || registry | minikube | disabled | minikube || registry-aliases | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) || registry-creds | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (UPMC Enterprises) || storage-provisioner | minikube | enabled ✅ | minikube || storage-provisioner-gluster | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Gluster) || volumesnapshots | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes ||-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|Next, list all running pod images in the cluster with:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces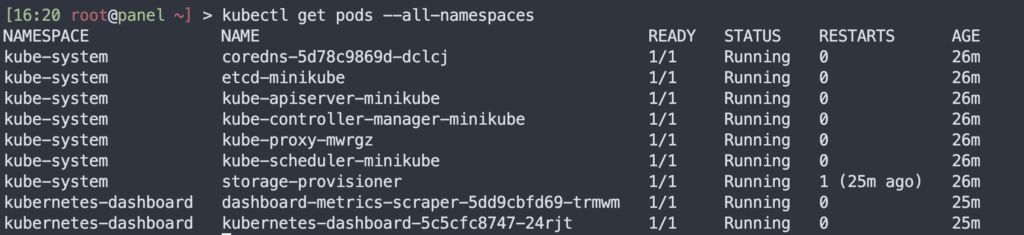
Now run the following command to get the Kubernetes Dashboard URL:
minikube dashboard --url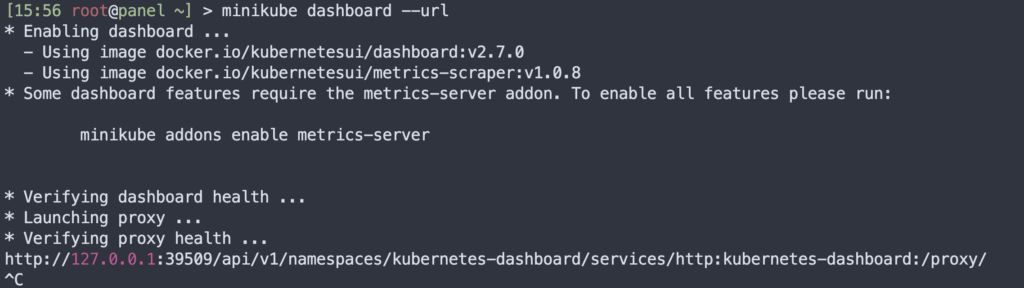
At this point, the Minikube Dashboard is installed and running on port 39509 on the server. However, it is only accessible from the local address. To access it from outside, run the following command:
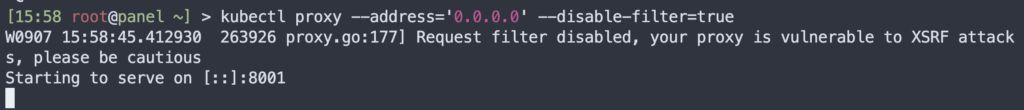
kubectl proxy --address='0.0.0.0' --disable-filter=trueNow open Chrome and visit:
http://your-server-ip:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/.
You will be redirected to the Kubernetes Dashboard, as shown below: